Working with data, Joining is the common operation.
Joining means combine i.e combine the data from two or more than two different sources on the basis of some conditions.
For performing such type of operation in R dplyr is the best option for doing so.
During this post, we will these key points.
- Types of Joins in R
- Syntax
- Joining on DataFrame
- Joining on tables
Types of Joins
There are six types of Joins in R :
- Inner Join (inner_join)
- Left Join (left_join)
- Right Join (right_join)
- Full Join (full_join)
- Semi Join (semi_join)
- Anti Join (anti_join)
Syntax
# Syntax of Joining in R
Join_type(x,y,by=condition)
/**
* x: dataframe1/table1
* y: dataframe2/table2
*/
Joins are basically applied on tables and in case of R files are to be considered as tables.
For a better understanding of joins, we are taking two files
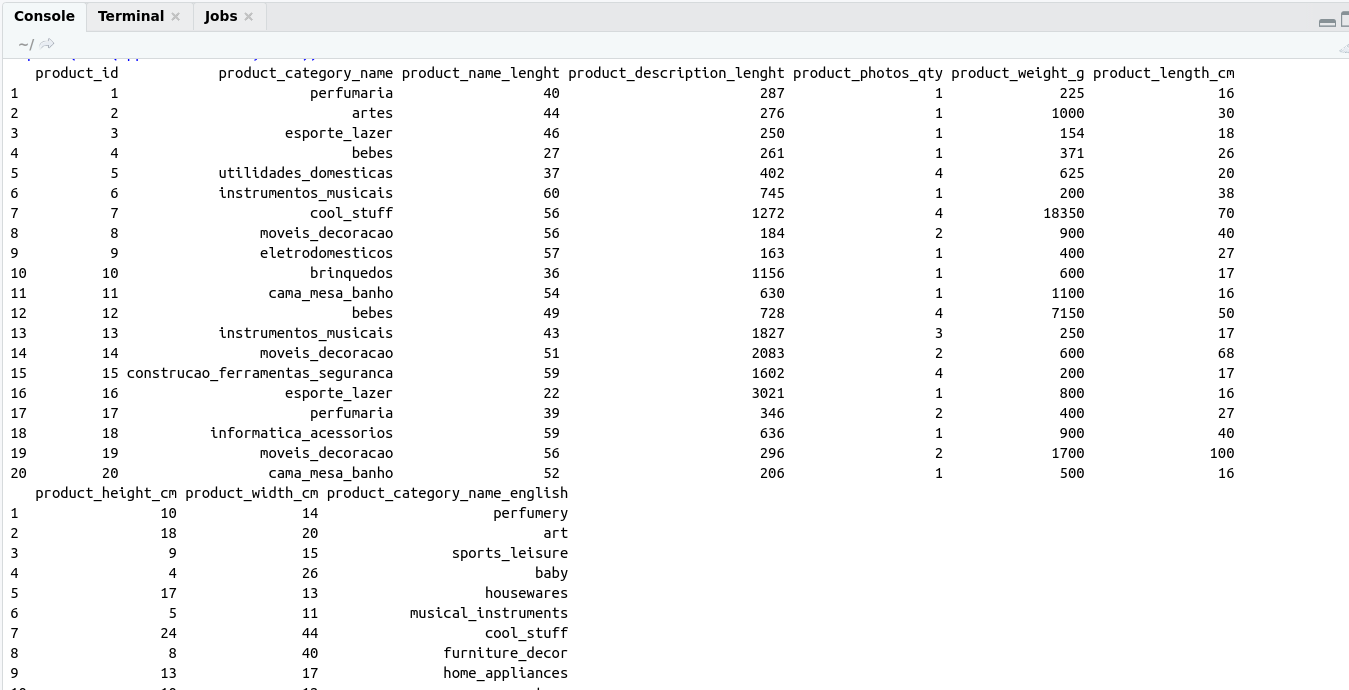
- Product_category_name.csv (product_category_name, product_category_name_english)
- product_dataset.csv(product_id,product_category_name,product_name_lenght, product_description_lenght, product_photos_qty, product_weight_g, product_length_cm, product_height_cm, product_width_cm)
You can download these files for your practice my GitHub account
As we know during applying joins on two different datasets or tables we need a common field on the basis of that we can be able to apply a join.
So, in this case, both files contain product_category_name so on the basis of that we can apply to join.
For using a CSV file as a table we are using command
# read csv file
read.csv(file_name)
So for applying joins on these two files at first, we have to consider these two files as two tables using read.csv() command. As shown below.
# load data
table1 <- read.csv("/home/dheeraj/Desktop/Blog_post/joins_in_r_using_dplyr/dataset/product_category_name.csv") # file location of Product_category_name.csv
table2 <- read.csv("/home/dheeraj/Desktop/Blog_post/joins_in_r_using_dplyr/dataset/products_dataset.csv") # file location of product_dataset.csv
Inner Joins
Syntax :
# inner join syntax
inner_join(x,y,by='condition')
Examples :
Select all columns
library(dplyr)
table1 <- read.csv("/home/dheeraj/Desktop/Blog_post/joins_in_r_using_dplyr/dataset/product_category_name.csv") # file location of Product_category_name.csv
table2 <- read.csv("/home/dheeraj/Desktop/Blog_post/joins_in_r_using_dplyr/dataset/products_dataset.csv") # file location of product_dataset.csv
appliedInnerJoin <- inner_join(table1,table2,by='product_category_name')
print(head(appliedInnerJoin,n =20))
OutPut:
Select specified columns
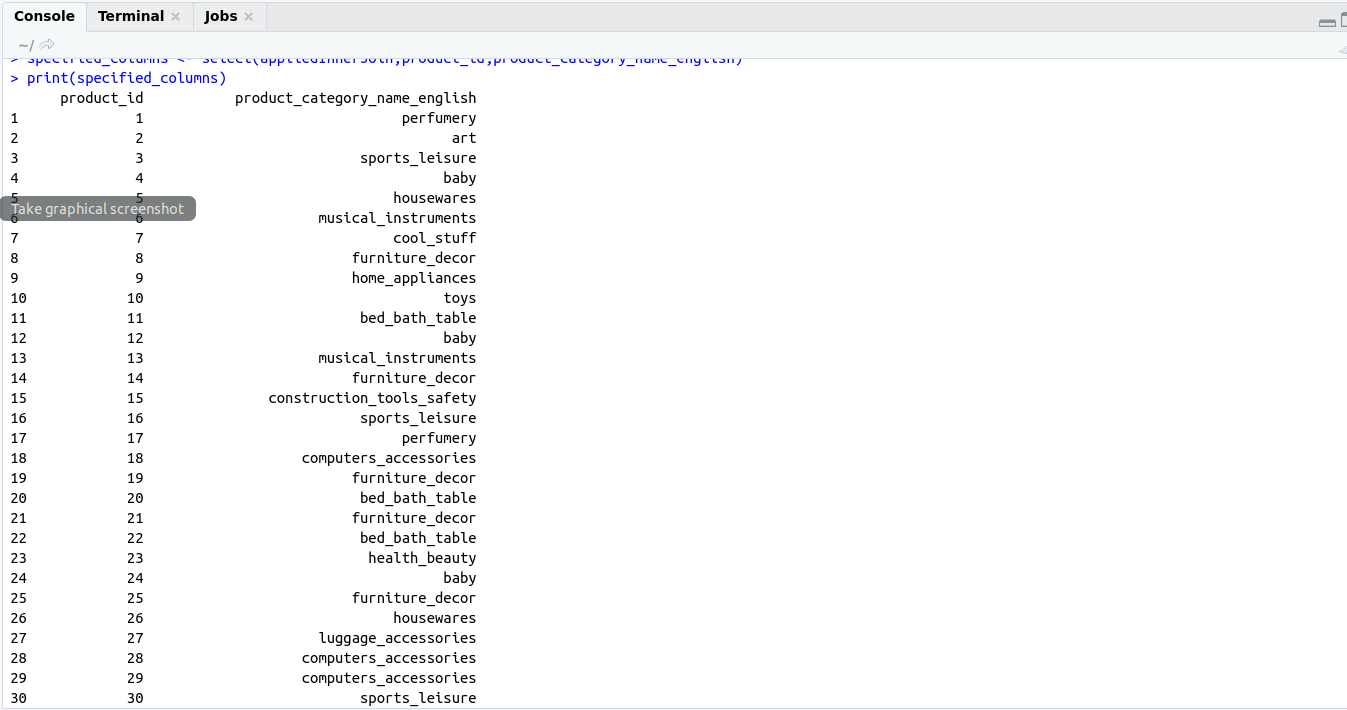
If we don’t want to extract all columns then we can select specified columns using select command.
Suppose In this after applying inner join on table1 and table2 we don’t want to extract all columns of these tables but also we want to extract only
product_id.product_category_name_english.
Then we can use select command of dplyr package (for more detail click here) and extract specified columns that we want to extract
Example
library(dplyr)
table1 <- read.csv("/home/dheeraj/Desktop/Blog_post/joins_in_r_using_dplyr/dataset/product_category_name.csv") # file location of Product_category_name.csv
table2 <- read.csv("/home/dheeraj/Desktop/Blog_post/joins_in_r_using_dplyr/dataset/products_dataset.csv") # file location of product_dataset.csv
appliedInnerJoin <- inner_join(table1,table2,by='product_category_name')
#select specified column
specified_columns <- select(appliedInnerJoin,product_id,product_category_name_english)
print(specified_columns)
OutPut:
left join
Syntax :
left_join(x,y,by='condition')
Example:
library(dplyr)
table1 <- read.csv("/home/dheeraj/Desktop/Blog_post/joins_in_r_using_dplyr/dataset/product_category_name.csv") # file location of Product_category_name.csv
table2 <- read.csv("/home/dheeraj/Desktop/Blog_post/joins_in_r_using_dplyr/dataset/products_dataset.csv") # file location of product_dataset.csv
# left join
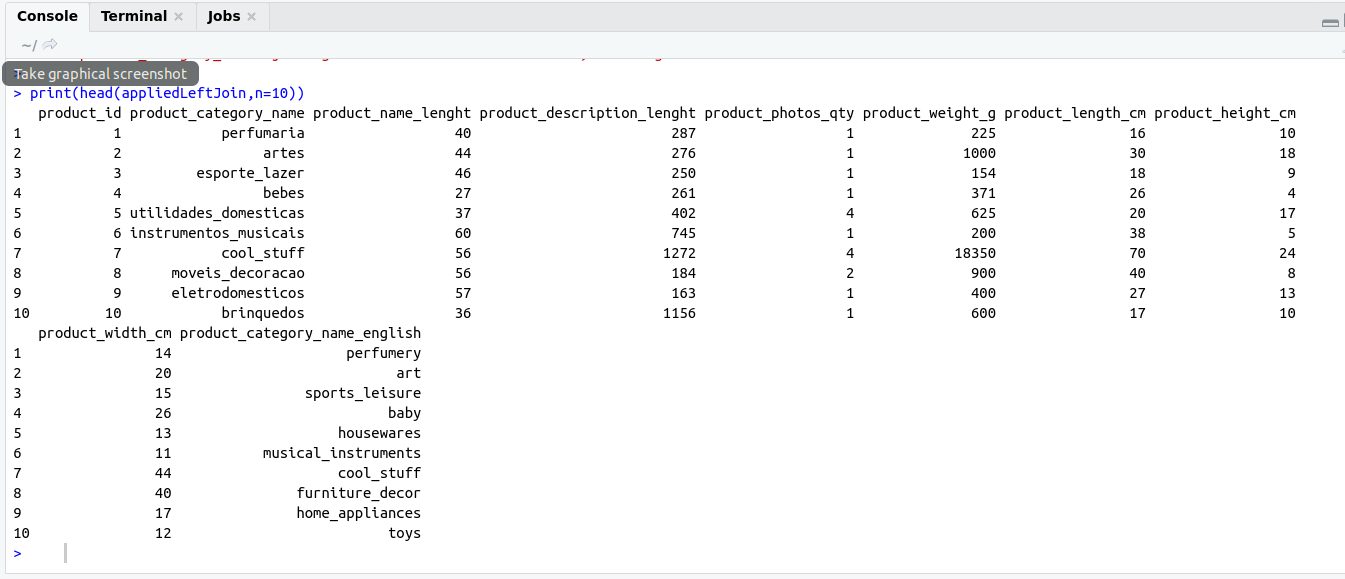
appliedLeftJoin <- left_join(table1,table2,by='product_category_name')<img src="http://www.krdheeraj.info/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/leftJoin.png" alt="" width="1345" height="579" class="alignnone size-full wp-image-496" />
print(head(appliedLeftJoin,n=10))
OutPut:
right join
Syntax :
right_join(x,y,by='condition')
EXample
library(dplyr)
table1 <- read.csv("/home/dheeraj/Desktop/Blog_post/joins_in_r_using_dplyr/dataset/product_category_name.csv") # file location of Product_category_name.csv
table2 <- read.csv("/home/dheeraj/Desktop/Blog_post/joins_in_r_using_dplyr/dataset/products_dataset.csv") # file location of product_dataset.csv
# left join
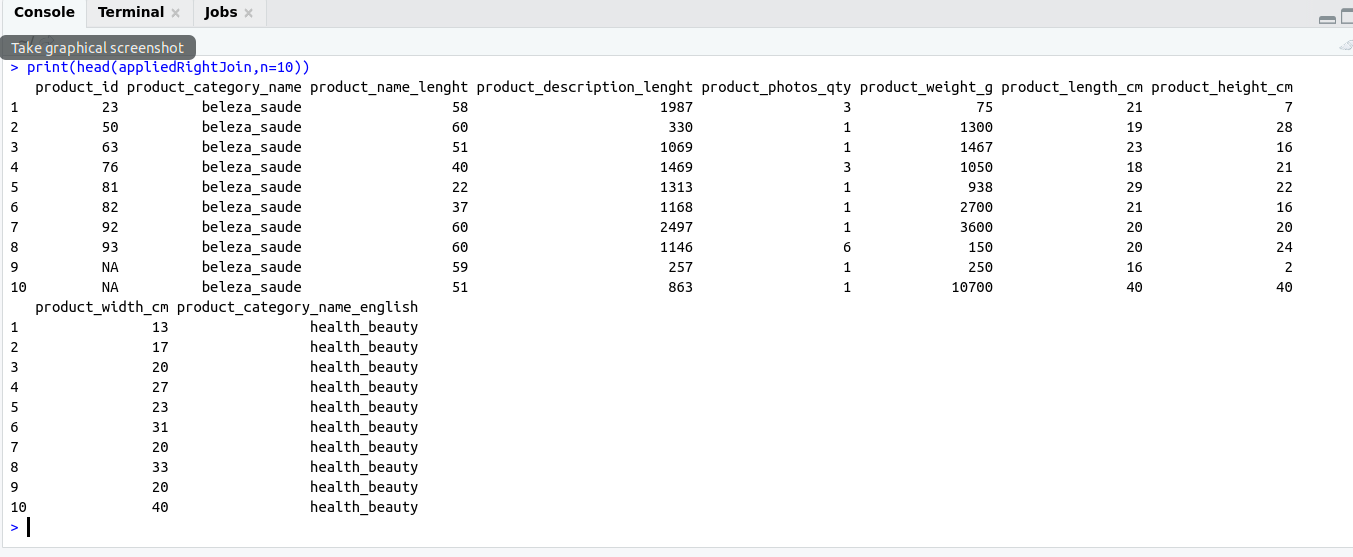
appliedRightJoin <- right_join(table1,table2,by='product_category_name')
print(head(appliedRightJoin,n=10))
Output: