Before going deep inside Word cloud, we first introduce ourselves from some important technical words, that we will use during this word cloud session in text mining .
Basically, the foundation of Bag Word testing is either TDM (Term Document Matrix) or DTM (Document Term matrix).
TDM (Term Document Matrix): The TDM is often the matrix used for language analysis. This is because you likely have more terms than authors or documents and life is generally easier when you have more rows than columns. So, In case of TDM word is represented as row and Document as Column.
Each Corpus word is represented as row and Document as Column.
How to create TDM from corpus?
| TDM Function |
Description |
| TermDocumentMatrix() |
Create Term Document Matrix |
DTM (Document Text Matrix): Transpose of TDM hence Document is a row, and each corpus is column.
How to create DTM from corpus?
| DTM Function |
Description |
| DocumentTermMatrix() |
Create Document Term Matrix |
Note: Among TDM and DTM which we going to use in our application that depends on scenario that either we want to take terms as a row as rows and document as column then, in that case, we have to pick TDM (Term Document Matrix) and vice-versa we have to focus on DTM (Document Term Matrix).
What is Word Cloud?
Word cloud is Text mining technique that allows us to highlights the most frequent keywords in paragraphs of text.
How to Create a Word Cloud?
There is a simple way for creating word cloud using packages like
tm: for creating corpus and cleaning data.
worldcloud: for constructing word cloud.
Steps for creating Word Cloud :
-
- Choose Text file
- Install packages and importing packages
- Reading file
- Converting a text file into corpus
- Clean Data and for that execute some commands
- Create a Term Document matrix
- Create your first cloud
Now without wasting our time we will follow the steps that we have discussed previously and achieve our target to construct word cloud. So, follow the steps
Choose Text file
At first, we choose a text file I have already taken a file that contains speeches of Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi I will attach this file for you so, that you can be able to practice with it.
Install Packages and importing packages
Install these packages for constructing cloud word for installing these packages you can use install.package() command like this way
#install packages
Install.packages(‘tm’)
Install.packages(‘wordcloud’)
Install.packages(‘RcolorBrewer’)
#load libary
library(‘tm’)
library(‘wordcloud’)
library(‘RcolorBrewer’)
Reading file
After installing and loading the library at first, we have need our text data on which we have to process. So, for loading text file and reading data, we will use these commands
# text file location
textFileLocation <- "F:\\Blog\\TextMining\\Word_word_text_mining\\text_speeches\\pm-modi-interacts-with-the-indian-community-in-kobe-japan.txt";
# load text file
textName <- file(textFileLocation,open="r")
# read text file
text_data <- readLines(textName)
Converting a text file into corpus
We can’t directly get word cloud directly from a text file but for constructing word cloud we have to at first convert our text data into the corpus. We can only on corpus for constructing word cloud. So, for constructing word cloud we follow these steps as we had also discussed in our previous post also.
Note: In this case, we are creating Vector Corpus for creating a word cloud.
# create corpus from text_data
textAsCorpus <- VCorpus(VectorSource(text_data))
Clean Data and for that execute some commands
Data cleaning is a more important part of any type of Data processing in this case also it is a very important part. For creating cleaning our corpus, we will execute these following commands
# corpus cleaning
clean_text <- tm_map(textAsCorpus,stripWhitespace)
clean_text <- tm_map(textAsCorpus,tolower)
clean_text <- tm_map(textAsCorpus,removeNumbers)
clean_text <- tm_map(textAsCorpus,removePunctuation)
Create a Term Document matrix
This is not a required step because we are considering corpus during creating a word cloud, but in this, I am showing you to calculate Term Document Matrix also.
#creating term Document matrix
tdm1 <- TermDocumentMatrix(clean_text)
# print term document message
print(as.matrix(tdm1))
OutPut:

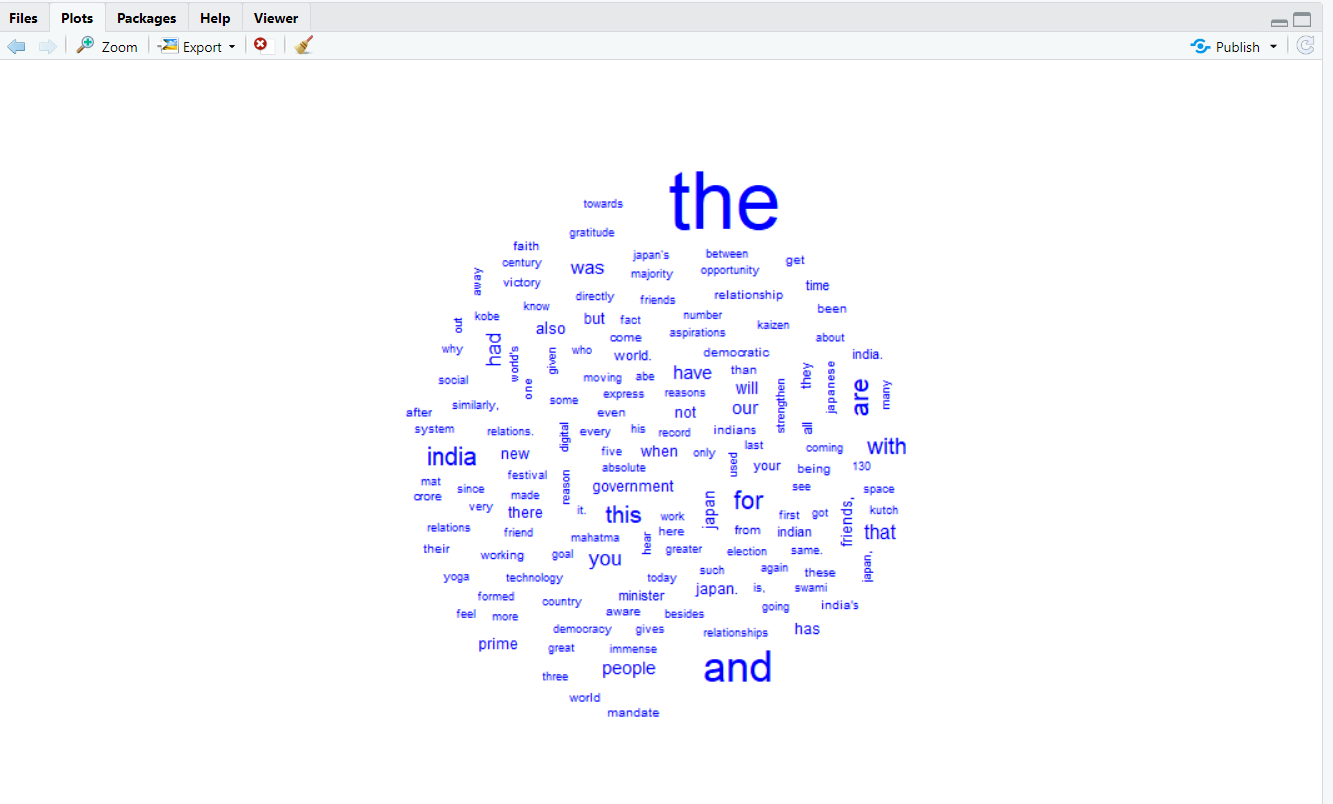
Create your first Word cloud
It is our final step for creating a word cloud. Now we have to use simple word cloud function of WordCloud package and add corpus inside function.
# create word cloud
wordcloud(clean_text, max.words = 500, colors = "blue")
OutPut:
Complete code
#install packages
Install.packages(‘tm’)
Install.packages(‘wordcloud’)
Install.packages(‘RcolorBrewer’)
#load libary
library(‘tm’)
library(‘wordcloud’)
library(‘RcolorBrewer’)
# text file location
textFileLocation <- "F:\\Blog\\TextMining\\Word_word_text_mining\\text_speeches\\pm-modi-interacts-with-the-indian-community-in-kobe-japan.txt";
# load text file
textName <- file(textFileLocation,open="r")
# read text file
text_data <- readLines(textName)
# create corpus from text_data
textAsCorpus <- VCorpus(VectorSource(text_data))
# corpus cleaning
clean_text <- tm_map(textAsCorpus,stripWhitespace)
clean_text <- tm_map(textAsCorpus,tolower)
clean_text <- tm_map(textAsCorpus,removeNumbers)
clean_text <- tm_map(textAsCorpus,removePunctuation)
#creating term Document matrix
tdm1 <- TermDocumentMatrix(clean_text)
# print term document message
print(as.matrix(tdm1)) # this not required so we can also comment
# create word cloud
wordcloud(clean_text, max.words = 500, colors = "blue")