In this post we will discuss about Redux and build a simple script for explaining Redux concept. Here, we are not implementing Redux in our React application. We will do so in our next post.
So, when we listened the term Redux then in our mind these question arise.
What is Redux ?
Why we use Redux?
How to use Redux?
In this post we will discuss all these questions one by one. At first we will discuss
What is Redux?
Redux is state management
Now another questioned arise in our mind:
What is state management?
Basically in React and other React like programming language we manage our data flow with help of state. And during this process we need to maintain global state i.e props value and local state i.e simply state value.
We can update local state but if we want to update our global state i.e value of global state i.e props then in that case Redux comes in Role.
Why we use Redux?
As I already explained Redux is used for state management. We can’t understand importance of Redux in smaller application.But in larger application it plays an important role. Where state management become more complex task.
How to use Redux?
Before using Redux we need to understand it’s terminology like
Store:
- Also called state tree
- Holds the whole state of your applications
Reducer:
- Also called Reducing function.
- It accepts an accumulation value and returns a new value.
- Reducer is basically used for reduce a collection of values down to a single value.
Note: Don’t call API calls into Reducers
Action
- An action is plain Object that represents an intention to change the state.
- Actions are the only way to get data into store
- Actions must have a type field which indicates the type of action being performed.
Subscribe
- It will be called anytime an action is dispatched, and some of state tree may potentially changed.
Dispatch
- Dispatch is function of Redux store.
- You can all store.dispatch to dispatch an action.
Now we are going to implement above Redux terminology in practical way. in this example we are not implementing Redux in any react application. But also we go through a simple node script.
So for that purpose at first we have to install Redux package in our application.
// install package
npm install --save redux
After that we will follow these steps :
Step 1: create a react_basic.js file
Step 2: Import redux package in your application
// Declare package
const redux= require('redux');
Step 3: Create a store
// create store
const redux= require('redux');
const createStore = redux.createStore;
//store
const store = createStore(rootReducer);
Note: We can’t get any thing without declaring reducer function
Step 4: Declare Reducer function
//Declare redux
const redux = require('redux');
const createStore = redux.createStore;
// create reducer
const rootReducer =(state,action)=>{
return state;
}
//store
const store = createStore(rootReducer);
console.log(store.getState())
OutPut:
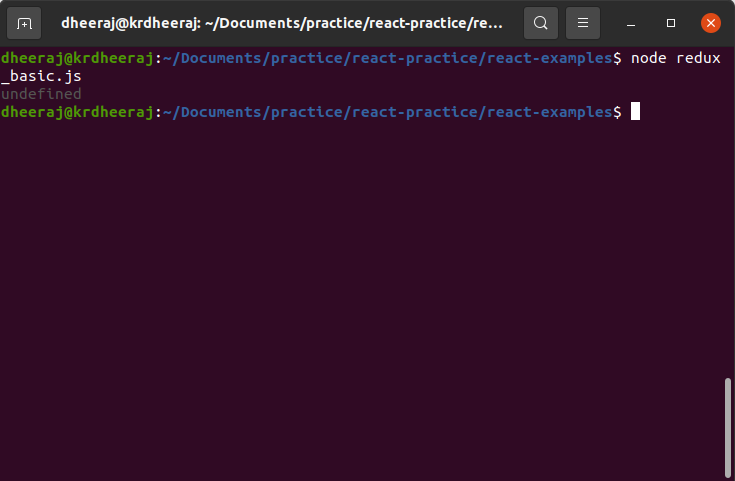
Note: Here we are getting undefined value because we have not initialised state yet. So at first we will initialised our initial state as shown below.
//Declare redux
const redux = require('redux');
const createStore = redux.createStore;
//initial state value
const initialState = {
counter: 0
}
// create reducer
const rootReducer =(state=initialState,action)=>{
return state;
}
//store
const store = createStore(rootReducer);
console.log(store.getState())
OutPut:
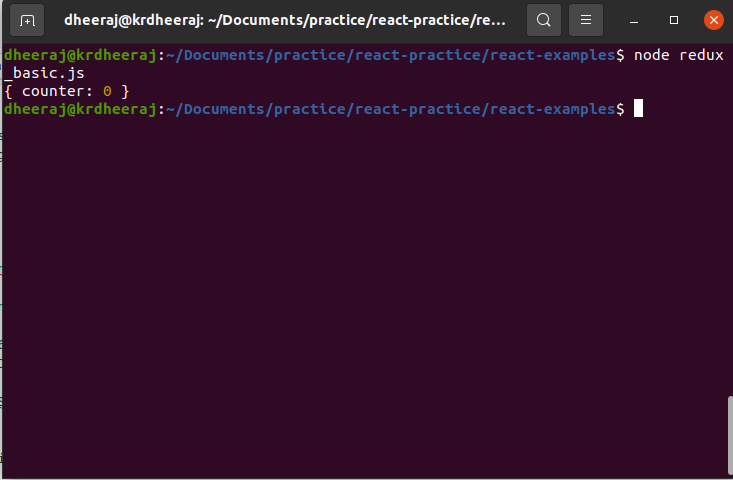
Step 5: Now dispatch our action
//Declare redux
const redux = require('redux');
const createStore = redux.createStore;
//initial state value
const initialState = {
counter: 0
}
// create reducer
const rootReducer =(state=initialState,action)=>{
return state;
}
//store
const store = createStore(rootReducer);
console.log(store.getState())
// Dispatch an action
store.dispatch({type:'ADD_COUNTER',value:15});
console.log(store.getState());
OutPut:
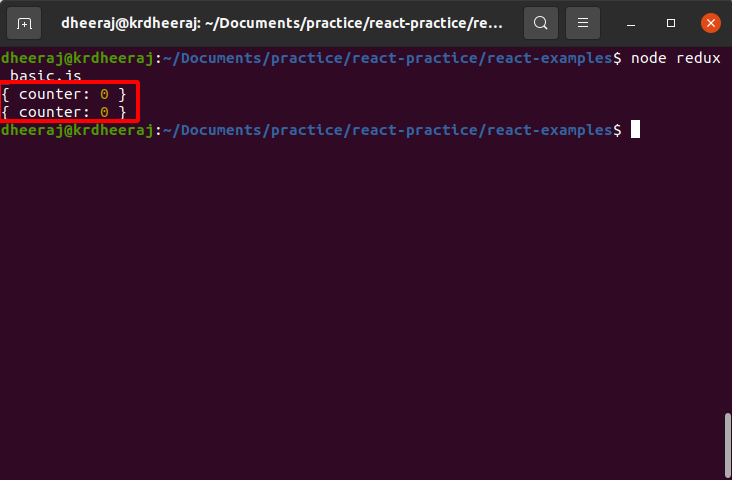
Note: We got same value in both console and reason for that we haven’t write any logic for that. So now we will write logic for our action type
Step 7: Add logic for ADD_COUNTER action type
we will write logic inside our reducer because reducer is being return our state
//Declare redux
const redux = require('redux');
const createStore = redux.createStore;
//initial state value
const initialState = {
counter: 0
}
// create reducer
const rootReducer = (state = initialState, action) => {
//ADD_COUNTER logic
if (action.type === 'ADD_COUNTER') {
return {
...state,
counter: state.counter + action.value
}
}
return state;
}
//store
const store = createStore(rootReducer);
console.log(store.getState())
// Dispatch an action
store.dispatch({type:'ADD_COUNTER',value:15});
console.log(store.getState());
OutPut:
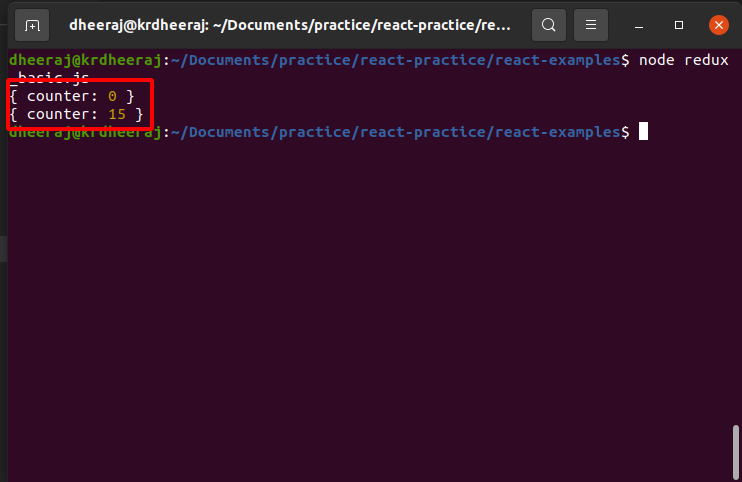
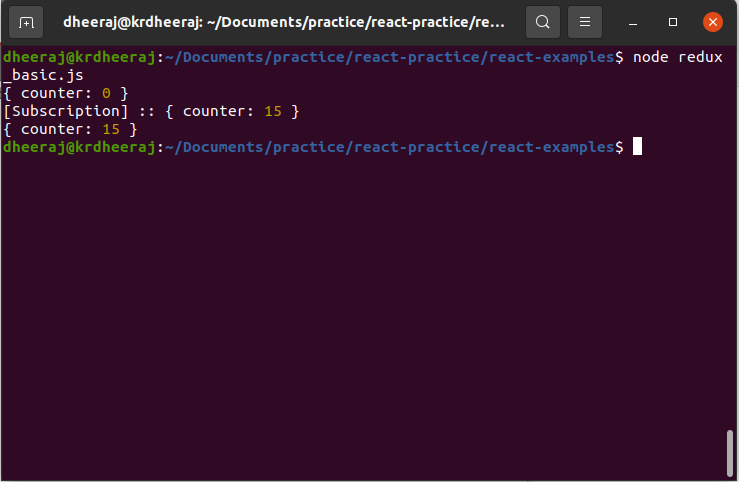
Step 8: Subscribe store
//Declare redux
const redux = require('redux');
const createStore = redux.createStore;
//initial state value
const initialState = {
counter: 0
}
// create reducer
const rootReducer = (state = initialState, action) => {
//ADD_COUNTER logic
if (action.type === 'ADD_COUNTER') {
return {
...state,
counter: state.counter + action.value
}
}
return state;
}
//store
const store = createStore(rootReducer);
//subscription
store.subscribe(() => {
console.log('[Subscription] ::', store.getState())
})
console.log(store.getState())
// Dispatch an action
store.dispatch({type:'ADD_COUNTER',value:15});
console.log(store.getState());
OutPut: